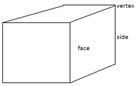
A cube is a special type of cuboid where each of the six faces are squares.
The volume of a cube = side x side x side = side3
![]()
The surface area of a cube = sum of the area of the 6 faces
Prisms
A prism always has two parallel and congruent faces called bases. The bases are themselves polygons. If the 2 bases of a prism are aligned to be one directly above the other, then it is a ?right prism?, otherwise, it is called an ?oblique prism?.
Below is an example of a right, ?triangular prism?:
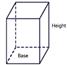
Below is an example of right, ?rectangular prism?:
Below is an example of an oblique rectangular prism:
![]()
The volume V of a prism is the area of the base B times the height h
![]()
The surface area of a prism is the sum of the area of all its faces (base faces and side faces).
Cylinders
A cylinder is very similar to a prism, in that it also has two parallel and congruent faces called bases. However, a cylinder?s bases are circles, not polygons. If the 2 bases of a cylinder are aligned to be one directly above the other, then it is a ?right cylinder?, otherwise, it is called an ?oblique cylinder?.
Below is an example of a right cylinder:
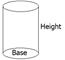
Below is an example of an oblique cylinder:
![]()
The volume V of a cylinder is the area of the base B times the height h
![]()
The surface area of a cylinder is the sum of the 2 base circles plus the area of its curved surface. You can think of the curved surface of a cylinder as a rectangle, with width the same as the height of the cylinder, and length the same as the perimeter of the base circle. Therefore, the surface area of a cylinder is:
![]()
Where A is the surface area of the cylinder, r is the radius of the base circle, and h is the height of the cylinder.