In this section, we study the reflection of light, focusing on how light is reflected in
- Plane mirror
- Concave mirror )
- Convex mirror (
- Convex lenses ()
- Concave lenses )(
Law of Reflection
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Remember that the angles are measured relative to the normal line.
Virtual Image
Virtual Image is an image formed by light coming from an apparent light source (behind the mirror); light is not coming from the actual image location (actual light source).

Real images are always on the same side as the object; virtual images are on the other side.
Images in Plane Mirror
- Distance from the object to the mirror is exactly the same as the image to the mirror
- The object-image line is perpendicular to the mirror surface
- Images are upright but flipped horizontally

Anatomy of Curved Mirrors
A concave or a convex mirror can be thought of as being a slice of a sphere. On the principal axis:
- C is the center of the curvature (sphere)
- F is focal point
- A is where principle axis and the mirror meets and is called vertex
- R is radius of curvature (sphere)
- f is distance between focal point F and vertex A (called focal length)
- f = R/2
Note: in convex mirror, focal length f is negative by convention.
Concave mirror:
Convex mirror:
The Mirror Equation
Suppose
- f is focal length
- So is object distance to mirror
- Si is image distance to mirror
- m is magnification ratio of image size to object size
- hi is image height and ho is object height.
We have:
1/f = 1/So + 1/Si
m = hi / ho = -Si / So
NOTE:
- f is positive for concave mirror and negative for convex mirror
- So is always positive
- Si is positive if image is real, ie, on the same side as object; Si is negative if image is virtual, ie, on the other side or behind the mirror
- m is positive if image is upright, m is negative if image is inverted (upside down)
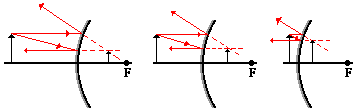
Applying the mirror equation to concave mirrors, there are 5 different scenarios:
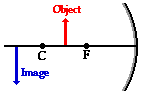
- Case 1: the object is located beyond the center of curvature (C) (beyond 2F): image is real, inverted, between F and C, and is smaller
- Case 2: the object is located at the center of curvature (C) (at 2F): image is real, inverted, at point C, and same size as object
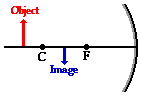
- Case 3: the object is located between the center of curvature (C) and the focal point (F) (between 2F and F): image is real, inverted, beyond C, and is larger
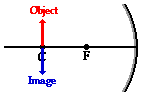
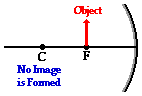
- Case 4: the object is located at the focal point (F) (at F): no image appears
- Case 5: the object is located between focal point (F) and the mirror (between F and mirror): image is virtual, not inverted, and is larger.
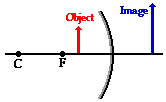
Refer to http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/Lesson-3/Image-Characteristics-for-Concave-Mirrors for more details.
Applying the mirror equation to convex mirrors, there is only 1 scenario: image is virtual, not inverted, and smaller than object.
Applying mirror equation to lens
The above mirror equations can be applied to lens. Assume thin lense approximation, and redefine:
- f is focal length (positive for convex lens, and negative for concave length),
- So is object distance to lens (always positive), and
- Si is image distance to lens (negative if image is virtual, or on the same side as object, positive if image is real, or on the other side, ie behind the lens)
There are 5 scenarios for convex lens:
There is 1 scenario for concave lens: